The most common form of environmental control for mechanical testing is temperature. The majority of test frames at SMaRT are fitted with a furnace for high temperature operation. Typically, three zone cylindrical resistance furnaces are fitted to creep frames, whilst a split design cylindrical furnace is used on the universal test frames, to facilitate loading. These furnaces operate up to temperatures around 1000°C. Additionally, SMaRT has a number of smaller split box furnaces capable of temperatures of 1300°C, which are also useful for applying heat to a small test section. A limited number of machines are equipped with induction heating systems which can apply a very precise heat affected zone.
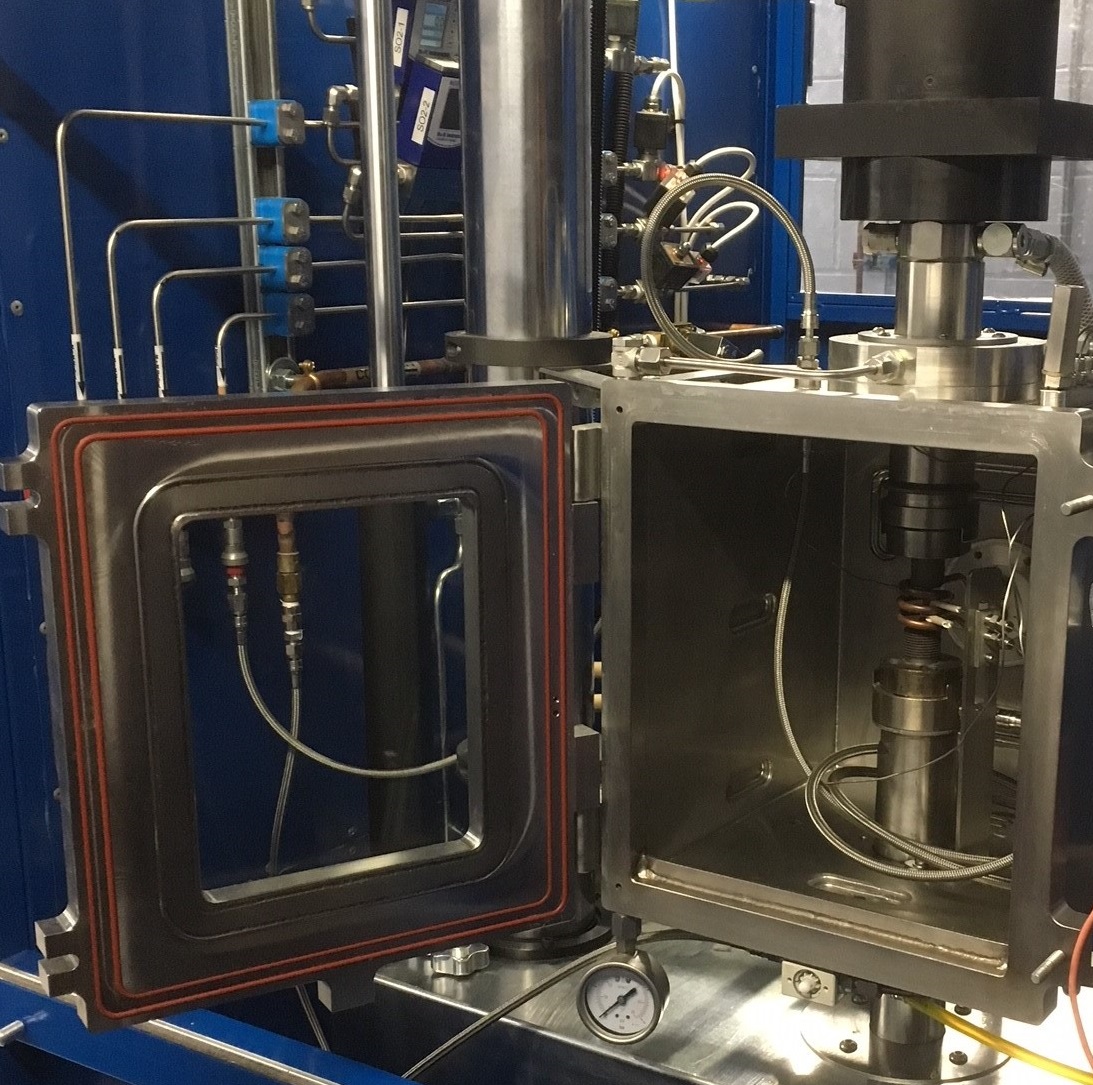
At SMaRT we have a dedicated corrosion laboratory, where by hot gas corrosion testing is conducted. This typically involves performing mechanical tests within an environment of up to 300ppm SO2 in air at elevated temperatures. A facility to assess salt corrosion is also available. Use of other gaseous environments are possible; Argon is often used to provide an oxygen free test environment.
SMaRT has the capability to test under vacuum or partial pressure (down to 1.3×10-6 mbar). The test frames are typically used for fatigue crack growth testing but can be utilised for various forms of dynamic testing.